Fish oil. You’ve seen it hyped up as some fat-burning miracle, but does it actually help with weight loss, or are you just throwing money at expensive capsules that make your burps smell like a fish market? Let’s cut through the nonsense and get straight to what omega-3 fatty acids actually do for body fat reduction and whether they belong in your weight-loss strategy.
Does Fish Oil Burn Fat? (Spoiler: Not Directly, But…)

No, fish oil itself won’t melt fat off your frame like a magic pill. But if you think that means it’s useless for weight loss, you’re missing the big picture. What omega-3s actually do is optimize the systems that control fat loss, making it easier to reduce body fat when combined with a proper diet and training program.
Here’s How It Works:
| Effect | How It Helps with Weight Loss |
|---|---|
| Reduces Inflammation | Chronic inflammation is linked to obesity and insulin resistance—two major fat-loss blockers. |
| Regulates Hormones | Supports proper hormone function, improving how your body uses fat for energy. |
| Controls Hunger | Omega-3s help reduce cravings and improve appetite regulation, making it easier to eat fewer calories. |
| Boosts Fat Oxidation | Helps your body tap into stored fat for fuel—especially when combined with exercise. |
| Improves Insulin Sensitivity | Poor insulin function leads to fat storage instead of fat burning. Fish oil helps reverse that. |
Bottom Line: Fish oil doesn’t burn fat directly, but it removes obstacles that make losing weight easier.
How Omega-3s Impact Fat Storage and Breakdown
If you’re carrying excess fat, especially around your midsection, it’s often due to hormonal imbalances, chronic inflammation, and poor insulin regulation. Omega-3s, found in wild-caught fish, fish oil supplements, and algae-based sources, play a critical role in fixing these metabolic issues.
1. It Helps Regulate Fat-Storing Hormones
Your body doesn’t just burn fat because you want it to. It has to be signaled to do so. Omega-3s help regulate the hormones involved in fat metabolism, including:
- Insulin – Lower levels mean your body is less likely to store fat and more likely to burn it for energy.
- Leptin – This hormone controls hunger and cravings. If leptin is off, you feel like eating 24/7. Omega-3s help restore balance.
- Cortisol – The stress hormone. High levels lead to belly fat accumulation. Omega-3s help keep it in check.
2. It Increases Fat Breakdown (Beta-Oxidation)
Studies indicate that fish oil enhances fat oxidation, meaning your body prefers to use fat as fuel instead of storing it. This effect is amplified when you combine fish oil with exercise, especially resistance training or high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
3. It Helps Reduce Inflammation (Which is Killing Your Fat Loss Progress)
Inflammation blocks weight loss. Period. Chronic inflammation makes fat cells resistant to burning fat, increases insulin resistance, and slows down metabolism.
Omega-3s are potent anti-inflammatory agents, making fat cells more responsive to burning fat. The result? More efficient weight loss, less joint pain, and better overall health.

Fish Oil vs. Other Fat Sources for Fat Loss
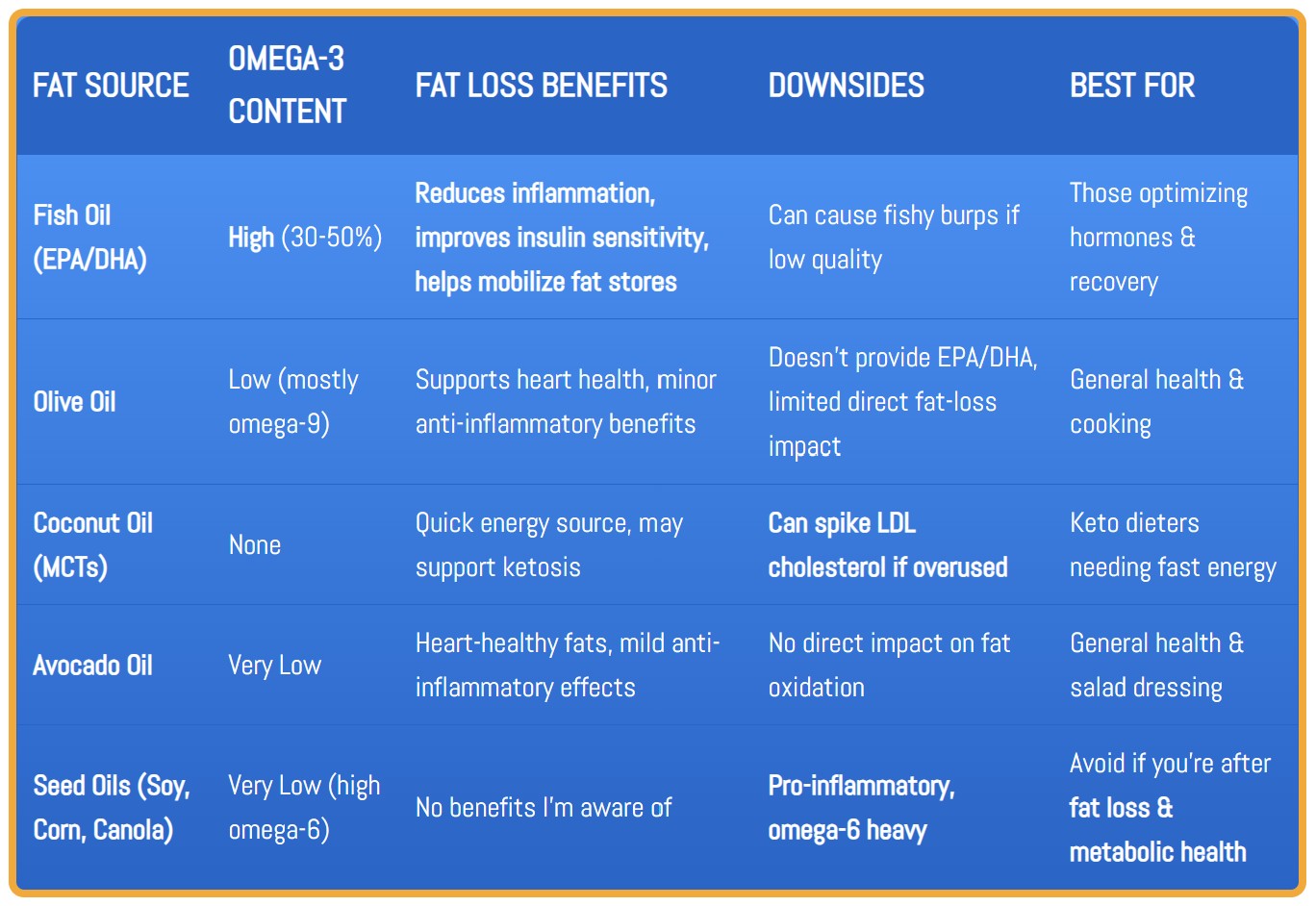

Takeaway: If you want fat loss, brain health, and anti-inflammatory benefits, fish oil crushes the competition. Coconut oil is a quick energy fix, but olive oil & avocado oil are better for overall health. Seed oils? Trash ‘em.
How to Take Fish Oil for Maximum Fat Loss
1. Choose the Right Type
Not all fish oils are created equal. Look for ones that contain high levels of EPA and DHA, the two main omega-3 fatty acids responsible for fat loss benefits.
- Best sources: Wild-caught fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and fish oil supplements.
- Avoid low-quality fish oil capsules that contain cheap filler oils and oxidized fats.
2. Dosage Matters
If you’re serious about results, take at least 2-3 grams of combined EPA and DHA per day. Most cheap fish oil supplements barely contain 300mg per capsule, which means you’d need 10+ pills to hit effective doses.
3. Timing – When to Take It
- With meals – Taking fish oil with meals improves absorption and reduces the chance of fish burps.
- Pre-Workout – If you train fasted, omega-3s may help mobilize fat stores for energy.
- Consistently – It’s not about timing; it’s about taking it every day.
4. Pair It with a Fat-Loss Friendly Diet
Fish oil won’t save you if your diet is garbage. Eat real food, focus on protein, keep carbs in check, and train hard. Fish oil enhances fat loss, but it’s not a free pass to eat like a dumpster fire.
A Table of Best Fish Oil Sources for Omega-3s (Ranked by Potency & Purity)
| Source | EPA + DHA (per 3.5 oz / 100g) | Mercury Risk | Best Form for Fat Loss | Other Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mackerel | 4,100 mg | Low | Whole fish, fish oil | High in vitamin D, selenium |
| Salmon (Wild-Caught) | 2,200 mg | Low | Whole fish, fish oil | Omega-3s + astaxanthin for skin & recovery |
| Sardines | 2,000 mg | Very Low | Canned or fresh | Portable, cheap, low mercury |
| Anchovies | 1,500 mg | Very Low | Whole fish, supplements | High in calcium |
| Herring | 1,700 mg | Low | Whole fish, smoked | Strong anti-inflammatory effects |
| Cod Liver Oil | 2,500 mg | Low | Liquid supplement | High in vitamin A & D |
| Tuna (Canned) | 800 mg | Medium | Light tuna (lower mercury) | Easy but lower in omega-3s |
| Shark / Tilefish | High, but toxic | Very High | Avoid | Biomagnification of heavy metals |
Takeaway: Small fish = best omega-3 bang for your buck with zero mercury issues. Wild-caught salmon & mackerel hit the sweet spot for powerful fat-loss benefits. Avoid shark & tilefish unless you like ingesting toxic metals.
Q&A: The Stuff Nobody Talks About
Q: Can Fish Oil Make You Gain Weight Instead of Lose It?
A: If you’re overeating calories, yes. Fish oil is still fat, which means it’s calorie-dense. One gram of fat = 9 calories. If you just add fish oil without reducing overall calories, you could gain weight instead of losing it.
Q: Are Some Fish More Beneficial Than Others for Fat Loss?
A: Yes. Smaller fish like sardines, anchovies, and mackerel have higher omega-3 content per gram and lower mercury levels. Larger fish (like swordfish, tilefish, and shark) accumulate more toxic materials, making them a bad choice for regular consumption.
Q: Can Fish Oil Supplements Replace Eating Fish?
A: Not entirely. Whole fish contain other beneficial nutrients like iodine, selenium, and protein that you won’t get from capsules. If you hate fish, supplements work—but whole food is always superior.
Q: What Happens If I Take Too Much Fish Oil?
A: If you overdo it, you might get digestive issues, nausea, or even excessive bleeding (because omega-3s act as a natural blood thinner). Stick to 2-3 grams of EPA/DHA per day unless you’re under medical supervision.
Q: Do Plant-Based Omega-3s Work for Fat Loss?
A: Not as well. Most plant-based omega-3s come from ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), which converts poorly into the active forms EPA and DHA. If you’re vegan, go for algae-based omega-3 supplements—they contain DHA, just like fish oil.
Final Verdict: Should You Take Fish Oil for Weight Loss?
If you’re serious about fat loss, yes—fish oil is a smart move. It won’t burn fat on its own, but it optimizes the conditions your body needs to lose fat more efficiently. Just make sure you’re pairing it with proper diet and training instead of hoping it magically melts fat while you sit on the couch.
Pro Tip: Take high-quality fish oil, eat a high-protein, low-calorie diet, and train hard. If you do that, fat loss gets easier, faster, and more effective.


