Creatine timing is the most over-complicated topic in supplement science. Here’s the truth: The “when” matters far less than the “that” — as in, that you take it consistently, every day. This 2026 Guide strips away the bro-science and marketing hype. We’ll cover the microscopic advantages of strategic timing, what the research actually says, and how to simplify your routine for maximum muscle and brain gains.

Disclaimer: You’re here to find a product that’ll get you results, and I’m here to help. Just a heads-up: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. If you buy through my links, I get a small commission at no added cost to you. It’s like I get a little something for doing the heavy lifting on research. Fair deal? Now, let’s get into the good stuff.
The Simple Truth About Creatine Timing
Creatine is not a pre-workout stimulant. It’s a chronic, intramuscular saturation supplement. Your goal is to keep muscle creatine phosphate stores consistently high. The half-life of creatine in your blood is short, but once it’s in the muscle, it stays put.
What The Research Says (And What It Doesn’t)
- Myth: You MUST take it post-workout.
- Reality: A few studies show a slight edge for post-workout absorption, likely due to increased blood flow and nutrient shuttling. The difference over the long term is negligible if your daily dose is consistent.
- Bottom Line: Daily consistency accounts for 99% of the benefit. The remaining 1% is splitting hairs for elite athletes.
“If you remember one thing: Saturate the muscle, don’t spike the blood. Taking 5 grams every single day matters infinitely more than trying to time a dose within a 30-minute ‘anabolic window.’ Miss a timing window? Just take it with your next meal.”
— Eugene Thong, CSCS
Optimal Timing Windows (If You Want to Optimize)
If you’re the type who wants every possible edge, here’s the hierarchy of timing strategies, from most to least impactful.
1. With a Meal (Carbohydrate + Protein)
Why it works: The insulin response from a meal enhances creatine uptake into muscle cells. This is the most practical and effective strategy for 95% of people.
- Best Meals: Post-workout meal, breakfast, or your largest carbohydrate-containing meal.
2. Post-Workout
The Edge: Combining the nutrient-shuttling effect of exercise-induced blood flow with a post-workout meal or shake. This is where that “slight edge” in the research comes from.
3. Pre-Workout
The Caveat: Taking creatine immediately before a workout does nothing for that session—it takes days to saturate stores. However, if it helps you remember your daily dose, it’s a fine habit.
The Final, No-BS Recommendation
Stop overthinking it. Use this decision tree:
- Step 1: Take 3-5 grams of a high-quality creatine monohydrate every day.
- Step 2: Take it with any meal you won’t forget. Your post-workout shake or breakfast are ideal anchors.
- Step 3: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- That’s it. Consistency and hydration are the only “hacks” you need.
“From a nutritional biochemistry standpoint, pairing creatine with a source of carbohydrates and protein is the only ‘timing’ strategy with a clear mechanism. For everyone else, adherence is the primary pharmacokinetic driver.”
— Charles Damiano, B.S. Clinical Nutrition
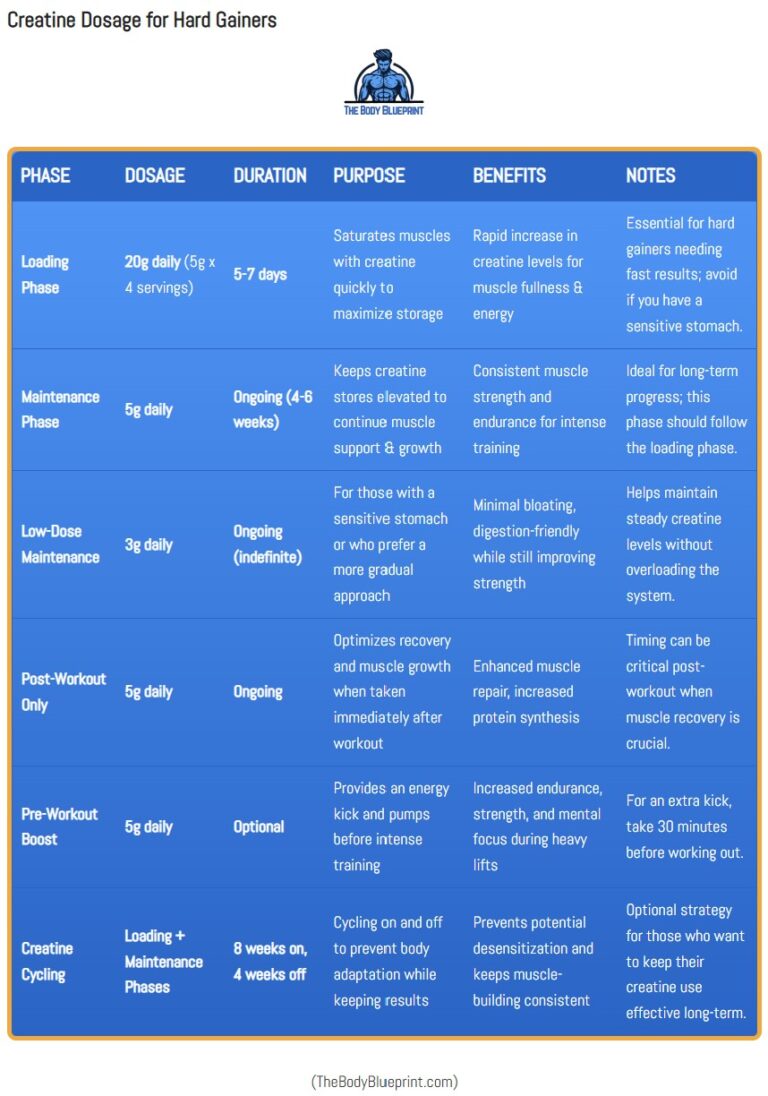
What About Loading Phases?
A loading phase (20g/day for 5-7 days) saturates muscles faster. If you time these larger doses, split them evenly throughout the day with meals. Otherwise, just take 5g/day—you’ll be saturated in about 3-4 weeks.
Top Creatine Picks: Timeless Quality Over Timing Gimmicks
All of these are pure creatine monohydrate. The “best” one is the one you’ll take consistently. Micronized versions mix easier.
| Product | Key Feature | Best For | Check Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimum Nutrition Micronized | Gold-standard purity & mixability | Anyone wanting a trusted, no-fuss brand | View on Amazon |
| Sports Research Micronized | Third-party tested, sourced from Germany | The purity-obsessed lifter | View on Amazon |
| Thorne Creatine | Exceptional quality control (often used in research) | Those with sensitive stomachs or who prioritize elite purity | View on Amazon |
| MuscleTech Platinum | Great value for size, highly micronized | The lifter wanting maximum cost-per-gram value | View on Amazon |
| Kaged Creatine HCl | Creatine Hydrochloride (different form) | Those who experience bloating with monohydrate* | View on Amazon |
*Note: HCl is not monohydrate. It may require a smaller dose. For a full breakdown, see our deep dive on alternative creatine forms.
“Don’t pay a premium for ‘advanced timing formulas.’ Buy pure creatine monohydrate, take it daily with food, and invest the money you saved into more protein or better quality meat.”
— Eugene Thong, CSCS
Related Creatine & Supplement Guides
- Creatine Comparison: Optimum Nutrition vs. MuscleTech
- Best Creatine for Men: An Evidence-Based Ranking
- Transparent Labs Creatine HMB Review: A Deep Dive
- Top 5 Creatine Supplements for Muscle Gain (2026)
The Iron Lexicon: Creatine Science Edition
- Muscle Saturation
- The primary goal of creatine supplementation: to maximize the concentration of creatine phosphate stored within muscle cells, enhancing energy production for high-intensity effort.
- Creatine Phosphate (CP)
- The high-energy molecule stored in muscles that rapidly replenishes ATP, the direct fuel for muscle contractions, during short, intense exercise.
- Loading Phase
- A short-term protocol (e.g., 20g/day for 5-7 days) designed to rapidly saturate muscle creatine stores, followed by a lower maintenance dose (3-5g/day).
- Micronized Creatine
- Creatine monohydrate processed into smaller particles, which dissolves and mixes more easily in liquid and may reduce the potential for stomach discomfort.
- Insulin-Mediated Uptake
- The process by which the hormone insulin, released in response to carbohydrate (and protein) intake, helps shuttle creatine from the bloodstream into muscle cells.
- Chronic Supplementation
- A long-term, consistent daily dosing strategy. The benefits of creatine are realized through sustained high muscle stores, not acute dosing.
- Half-Life (in blood)
- The time it takes for the concentration of a substance in the blood to reduce by half. Creatine’s short blood half-life is why intramuscular storage, not blood levels, is the focus.