Forget flashy packaging and influencer endorsements. Back in the 70s, bodybuilders relied on classic supplements that got straight to the point: building muscle, shredding fat, and sculpting the perfect physique. These weren’t just trendy powders—they were the tools legends like Arnold Schwarzenegger, Franco Columbu, and Frank Zane used to dominate the stage. If you’re serious about bodybuilding or just curious about what worked for the golden-era competitors, this guide has everything you need to know. Let’s dive into the old-school must-haves that fueled the biggest names in fitness history.
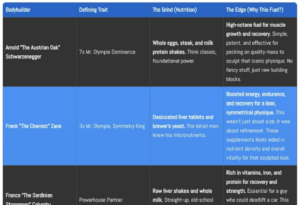
1970s Bodybuilders and Their Go-To Foods or Supplements (TABLE)
(Click to Save)
Classic Bodybuilding Supplements Table: What Worked in the 70s
| Supplement | What It Is | Benefits | How to Use | Cautions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Egg Protein | Protein powder made from egg whites. | Lactose-free, high-quality amino acids for muscle repair and growth. | Mix with water or milk; use post-workout or as a meal replacement. | Not suitable for those with egg allergies. |
| Milk Protein | Casein or whey protein powder derived from milk. | Slow digestion for overnight recovery; rich in essential amino acids. | Drink before bed or between meals for sustained muscle support. | Avoid if lactose-intolerant unless labeled lactose-free. |
| Liver Tablets | Compressed tablets of desiccated liver. | Boosts red blood cell production, endurance, and muscle recovery. | Take with meals or throughout the day for steady energy. | Check labels for allergens or cross-contamination risks. |
| Brewer’s Yeast | Nutritional yeast rich in B-complex vitamins, selenium, and chromium. | Supports metabolism, energy production, and recovery. | Take as tablets or mix the powder into smoothies or shakes. | May cause bloating in some individuals; start with small doses. |
| Desiccated Liver | Powdered form of dried liver, often used in shakes. | High in iron, B vitamins, and protein for maximum recovery. | Mix with water or add to homemade shakes for nutrient-packed drinks. | Handle carefully due to cross-contamination risks in manufacturing. |
| Vitamin B12 | A key vitamin for red blood cell production and energy metabolism. | Improves endurance and muscle oxygenation during intense training. | Take in supplement form or as part of a multivitamin. | Excessive doses may cause side effects like headaches or dizziness. |
| Multivitamins | Comprehensive supplements covering essential vitamins and minerals. | Fills nutritional gaps, supports immunity, and enhances recovery. | Take daily with meals for better absorption. | Choose reputable brands to avoid poor-quality formulations. |
| Iron Supplements | Provides dietary iron to enhance oxygen transport in the blood. | Reduces fatigue and improves performance during high-intensity training. | Take as directed by a doctor or based on dietary needs. | Overdosing can lead to iron toxicity—consult a GP if unsure. |
| Blended Liver & Organ Meats | Homemade blend of cooked liver, organ meats, garlic, and lemon. | Extremely nutrient-dense for muscle repair and overall health. | Blend cooked ingredients; drink fresh for maximum nutrition. | Strong taste; may not be suitable for everyone. |
| Raw Liver Shakes | Shakes made from raw liver blended with milk or water (a hardcore classic). | High in iron, protein, and fat-soluble vitamins like A and D. | Blend fresh raw liver with liquid; consume immediately. | Risk of foodborne illness—use only if the liver is fresh and from a trusted source. |
| Brewer’s Yeast Tablets | Compressed yeast tablets packed with B vitamins and minerals. | Boosts energy and protein metabolism; supports overall recovery. | Take with meals or add to shakes as a convenient supplement. | Start small to gauge tolerance, as large doses may cause gastrointestinal issues. |
| Fish Powder | Powdered fish product rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein. | Improves joint health and provides a unique protein source. | Add to shakes or meals; use sparingly to avoid strong taste overpowering your food. | Ensure proper storage to prevent spoilage or contamination. |
How This Table Helps
- Quick reference: Everything you need to know about classic supplements at a glance.
- Practical tips: Avoid wasting time on guesswork.
- Risk awareness: Play it safe with these insights.
Use this to optimize your old-school supplement game and level up like the golden-era pros.
Protein Powders: The Foundation of Every Classic Physique
Protein is non-negotiable if you want to build muscle. In the 70s, protein powders weren’t the highly-processed, flavor-loaded shakes we have today. They were simple, effective, and often gritty.
- Egg Protein
- Made from egg whites.
- High-quality protein source (packed with all essential amino acids).
- Bodybuilders loved it because it was lactose-free, making it ideal for anyone with milk allergies.
- Milk Protein
- Often made from casein or whey.
- Digests slower than egg protein, making it great for overnight recovery.
- Rich in essential amino acids for muscle repair.
Pro Tip: If you’re already hitting your daily protein intake, adding these powders might not make a noticeable difference. But if your diet’s lacking, they’re a game-changer.
Liver Tablets: A Forgotten Secret Weapon
Liver tablets were a staple for bodybuilders looking to pack on lean mass. They’re not sexy, but they’re packed with iron, vitamin B12, and amino acids.
- What are they?
Small, compressed tablets made from desiccated (dried) liver. - Why use them?
They boost red blood cell production, increasing oxygen delivery to muscles. This means better pumps, improved recovery, and enhanced endurance.
Warning: Check the label if you’re allergic to any ingredients. There’s always the risk of cross-contamination during manufacturing.
Brewer’s Yeast: Nature’s Multivitamin
Brewer’s yeast tablets were another classic staple. Rich in B-complex vitamins, chromium, and selenium, these little powerhouses gave bodybuilders the energy they needed for intense training.
- Best for: Supporting metabolism and recovery.
- How to take: Usually in tablet form, sometimes mixed into shakes for added nutrition.
Desiccated Liver: Hardcore Nutrition in Powder Form
Desiccated liver was like liver tablets but ground into a powder. It was often mixed with water or blended into raw liver shakes (yeah, they weren’t messing around).
- Nutritional profile: Packed with iron, protein, and fat-soluble vitamins like A and D.
- Why use it? For maximum recovery and muscle-building potential.
Vitamin Supplements: The Micronutrient Advantage
Old-school bodybuilders didn’t just focus on macros—they knew micronutrients were just as important.
- Vitamin B12
- Boosts red blood cell production.
- Supports energy levels and endurance during grueling workouts.
- Multivitamins
- Provided a safety net to cover any dietary gaps.
- Focused on key nutrients like vitamin C, zinc, and magnesium for immunity and recovery.
- Iron Supplements
- Essential for oxygen delivery to muscles.
- Helped combat fatigue from intense training.
Homemade Blends: Old-School DIY Nutrition
Back then, bodybuilders weren’t afraid to get their hands dirty. They made homemade blends packed with nutrients.
- Blended Liver and Organ Meats
- Why? Organ meats are some of the most nutrient-dense foods on the planet.
- How? Blend cooked liver with water, garlic, and a touch of lemon juice.
- Raw Liver Shakes
- The ultimate hardcore supplement.
- Warning: Eating raw liver carries obvious risks like allergens and potential cross-contamination. Proceed cautiously.
Health Food Store Supplements: Affordable Alternatives
In the 70s, big-brand supplements weren’t everywhere. Bodybuilders often turned to health food stores for natural, no-frills solutions.
- Brewer’s Yeast Tablets
- Rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Boosts energy and supports protein metabolism.
- Fish Powder
- A niche supplement loaded with omega-3 fatty acids for joint health.
- Often added to homemade shakes for extra protein and healthy fats.
Q&A: Rare Questions You Haven’t Thought Of
A: Absolutely. Supplements like protein powders and liver tablets aren’t just for men. Women who want to boost recovery and energy levels can benefit too. Just consult your GP if you’re unsure about dosage.
A: Liver is a nutritional powerhouse. It’s packed with iron, B12, and amino acids—all essential for muscle growth and recovery. Back then, they didn’t have today’s fancy powders, so they relied on what worked.
A: Yes. Some products, like raw liver, come with risks like allergens or cross-contamination. Always check labels and proceed cautiously if you’re allergic or have a medical condition.
A: Sure. Modern products are more refined and convenient. But if you want to go full-on classic for the nostalgia and simplicity, stick with the old-school approach.
Final Thoughts: Should You Go Old-School?
The classic bodybuilding supplements from the 70s weren’t flashy, but they worked. They focused on nutrition, recovery, and building a rock-solid physique. If you’re tired of overhyped products and want to experiment with what legends used, these are worth a shot.
Just remember: Supplements are tools. They’ll help if your training and diet are on point. If they’re not? Fix those first.
YOUR NEXT STEPS: