Bodybuilding didn’t just shape physiques—it transformed the way the world saw food, fitness, and health. From protein-packed diets to the rise of supplements, the 20th century was a revolutionary period that merged nutritional science with gym culture. Let’s dig into how bodybuilding nutrition left a lasting mark on our kitchens and beyond.
The Rise of Bodybuilding Nutrition
| Era | Key Events & Trends |
|---|---|
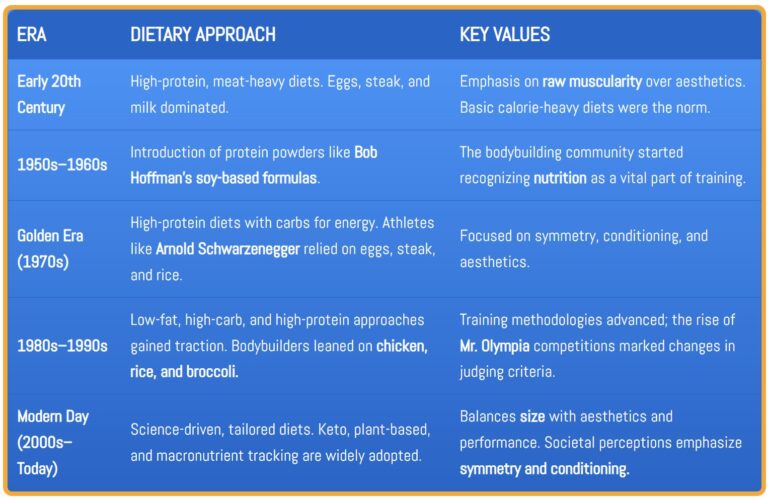
| Early 1900s | Strongmen like Eugen Sandow promoted whole foods and calorie-dense meals for strength. |
| Mid-Century | The “Golden Era” of bodybuilding introduced the concept of macronutrient tracking (protein, carbs, fats). |
| 1970s | Icons like Arnold Schwarzenegger popularized protein shakes and bulking/cutting cycles. |
| 1980s-1990s | The supplement industry exploded, introducing creatine, amino acids, and meal replacements. |
How Nutrition Revolutionized Bodybuilding
- Protein as King:
- By the 1950s, protein was hailed as the muscle-building macronutrient.
- Early bodybuilders consumed steak, eggs, and milk in bulk.
- Carb Control:
- The 1970s emphasized low-carb diets during cutting phases, inspired by Vince Gironda’s philosophies.
- Athletes fine-tuned carb intake to balance muscle glycogen and fat burning.
- Meal Timing:
- Frequent meals (5-7 per day) became the norm, designed to maintain an anabolic state.
- Supplements Take Center Stage:
- Whey protein became a household name by the 1990s.
- Brands like Weider Nutrition pioneered pre-workouts and protein powders.
Cultural Ripple Effects
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Pop Culture Influence | Movies like Pumping Iron (1977) made bodybuilding diets mainstream. |
| Fitness Magazines | Publications like Muscle & Fitness taught the masses about macronutrients and meal plans. |
| Global Trends | Countries like India and Brazil embraced bodybuilding nutrition as part of modern fitness. |
| Diet Fads | High-protein diets (e.g., Atkins Diet) found roots in bodybuilding meal plans. |
Key Figures in Bodybuilding Nutrition
| Name | Contributions |
|---|---|
| Eugen Sandow | Advocated for balanced, whole-food diets in the early 1900s. |
| Vince Gironda | Promoted low-carb, high-protein diets for muscle definition in the 1960s. |
| Joe Weider | Introduced commercial protein powders and training supplements to the public. |
| Arnold Schwarzenegger | Elevated the importance of nutrition for mass and symmetry during his reign. |
Modern Takeaways from 20th-Century Nutrition
- Macronutrient Focus: The balance of protein, carbs, and fats continues to be foundational for bodybuilders.
- Supplement Usage: Modern formulas stem from the early experimentation with protein powders and amino acids.
- Cultural Shifts: Today’s obsession with meal prep and calorie tracking owes much to bodybuilding pioneers.
FAQs About Bodybuilding Nutrition
Q: How did bodybuilding diets differ before and after the 1950s?
A: Early 20th-century athletes ate hearty meals like steak and potatoes, focusing on strength and bulk. Post-1950s, science entered the equation, and bodybuilders began tracking macronutrients with precision. This marked the transition from eating for energy to eating for physique optimization.
Q: When did protein shakes become popular?
A: Protein shakes emerged in the 1970s, thanks to brands like Weider Nutrition. They were crude compared to today’s formulas—mostly powdered milk and soy—but they set the stage for modern whey proteins.
Q: Was creatine used in the 20th century?
A: Not until the 1990s! It hit the market after studies showed it boosted strength and recovery. Creatine’s late entry highlighted how bodybuilding nutrition evolved alongside science.
Rare or Unusual Questions
Q: Did strongmen in the early 1900s eat differently from modern bodybuilders?
A: Absolutely. Back then, it wasn’t about macros or supplements. Strongmen like Eugen Sandow consumed hearty, calorie-dense meals, including pork chops, whole milk, and bread, to fuel their massive lifts. Contrast that with today’s pre-measured meals packed in Tupperware, and you’ve got a world of difference.
Q: What role did eggs play in Golden Era bodybuilding diets?
A: Eggs were a superfood before anyone knew the term. Guys like Vince Gironda swore by raw eggs, sometimes drinking 12-36 eggs a day for their high protein and fat content. The approach sounds extreme now, but it worked before modern supplements became available.
Q: How did bodybuilding nutrition influence military rations?
A: During the 20th century, as bodybuilding and nutritional science advanced, high-protein meal planning influenced military rations. The U.S. military incorporated protein bars and powdered drinks into field kits, inspired by the convenience and effectiveness of bodybuilding supplements.
Q: Were cheat meals always part of bodybuilding nutrition?
A: Surprisingly, no. Early bodybuilders didn’t indulge in cheat meals because their diets were already simple and wholesome. The concept became popular in the 1980s, when structured dieting gained traction, and a cheat meal served as both a psychological and metabolic break.
Summary of Key Points
- Pioneering Figures: Vince Gironda, Arnold Schwarzenegger, and Joe Weider transformed how bodybuilders approached food.
- Nutritional Pillars: Protein-focused diets, frequent meals, and supplements like whey revolutionized training outcomes.
- Global Influence: Bodybuilding nutrition influenced everyday diets, from Atkins to modern meal-prep culture.
Pro Tip: To truly understand bodybuilding nutrition, think beyond food—it’s about the relationship between diet, discipline, and ambition.